Predicting T Cell Mitochondria Hijacking from Tumor Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data with MitoR
Published in Mathematics, 2025
Authors: Anna Jiang#, Chengshang Lyu#, Yue Zhao*.
DOI: 10.3390/math13040673
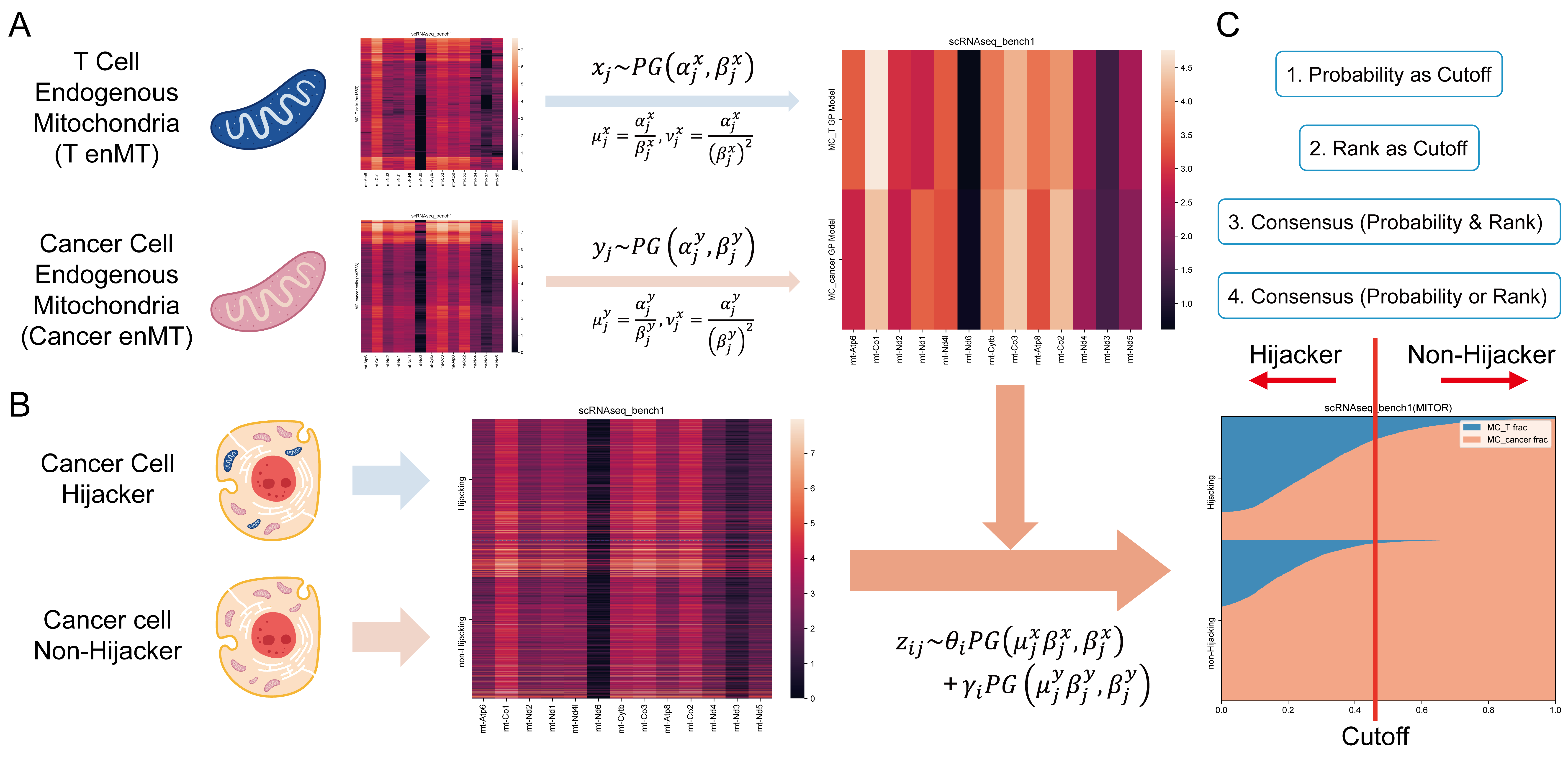
- Abstract: T cells play a crucial role in the immune system by identifying and eliminating tumor cells. Malignant cancer cells can hijack mitochondria (MT) from nearby T cells, affecting their metabolism and weakening their immune functions. This phenomenon, observed through co-culture systems and fluorescent labeling, has been further explored with the development of the MERCI algorithm, which predicts T cell MT hijacking in cancer cells using single-cell RNA (scRNA) sequencing data. However, MERCI is limited by its reliance on a linear model and its inability to handle data sparsity. To address these challenges, we introduce MitoR, a computational algorithm using a Poisson–Gamma mixture model to predict T cell MT hijacking from tumor scRNA data. In performance comparisons, MitoR demonstrated improved performance compared to MERCI’s on gold-standard benchmark datasets scRNA-bench1 (top AUROC: 0.761, top accuracy: 0.769) and scRNA-bench2 (top AUROC: 0.730, top accuracy: 0.733). Additionally, MitoR showed an average 4.14% increase in AUROC and an average 3.86% increase in accuracy over MERCI in all rank strategies and simulated datasets. Finally, MitoR revealed T cell MT hijacking events in two real-world tumor datasets (basal cell carcinoma and esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma), highlighting their role in tumor immune evasion.